SEO can refer to either the practice of optimizing a website or webpage for better search result rankings (optimization) or to the person doing the optimization (optimizer).
While most of the time SEO refers to optimization in Google, it can also refer to search ranking optimization in Bing, YouTube, and even Amazon.
SEO can broadly be categorized into two categories: local SEO campaigns and general or national SEO campaigns. If your business is recognized by Google as a local business (anything from a lawyer to a CBD dispensary) then you will most likely want to rank high for local searches, ie “magic wand store Knoxville”. In this case you be competing mostly other local businesses. If you have an e-commerce business or if your business category isn’t recognized by Google as a local business category then you will be competing from any other business in your category on a national or international level. At the end of the day, the difficulty of achieving SEO goals depends largely on how hard your competition wants to be #1 on Google.
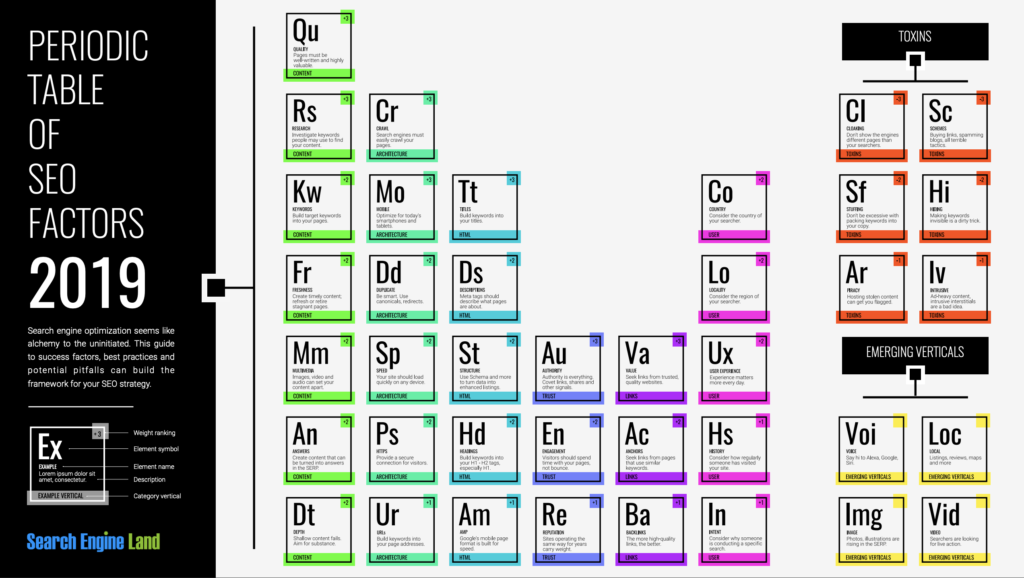
There are around 30 factors that can affect the ranking of site in Google. Some of the most important ones are:
- Quality: The overall quality of your site. Is the content relevant? Are there few to no spelling errors, etc?
- Inbound Links: Do other sites that are reputable link to your site?
- Site Structure: Are all the Is dotted and Ts crossed?
- Pagespeed
- Mobile Optimization: Does your site look good on a phone? Can users navigate easily on a phone?
- Google Reviews (for Local SEO)
- Google My Business Page quality (for Local SEO): Is your information accurate? Is the business in the correct category? Are there recent posts?
- Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) consistency
Search Engine Land publishes an SEO periodic table of elements each year that ranks the importance of these: